Cemeteries
The Basics: Types and FeaturesLooking for a Cemetery?
Click on Find Services to locate cemeteries, funeral homes, monument dealers, and other funeral service providers in your area.
A Final Resting Place
A cemetery is the place where the dead are buried or interred — a “final resting place” for the deceased. In the past, people were buried on family property, in church yards, or in community cemeteries.
Cemeteries eventually became privately owned businesses organized “for-profit”; however, some States prohibit for-profit cemeteries. Religious, municipal, and veteran cemeteries are organized on a not-for-profit basis. The result is a diverse mix of styles, sizes, and ownership structures. The grounds and products typically include:
- Offers caskets, outer burial containers, and grave markers or monuments.
- Holds services in their chapel or at the graveside.
- Opens and closes the grave.
- Installs the grave marker (although a monument company may do this installation).
Cemeteries and other funeral service providers work together to coordinate funeral plans. For example, the Funeral Director is generally responsible for the following:
- Procession to the gravesite.
- Services on the grounds.
- Return transportation for the family.
A distinctive place for eternal use
Cemeteries

With their natural beauty, cemeteries are where survivors can return over time to remember and honor their loved ones.
Features

The grounds may be adorned with sculptures, memorials, and other decorative elements.
Roadways

Besides these features, cemeteries also differ in the basic elements such as the quality of their roadways, irrigation and maintenance.
Memorial Parks
 Memorial parks are distinguished from traditional cemeteries by their more park-like appearance due to the absence of upright monuments. These properties allow only flush markers.
Memorial parks are distinguished from traditional cemeteries by their more park-like appearance due to the absence of upright monuments. These properties allow only flush markers.
Traditional Cemeteries
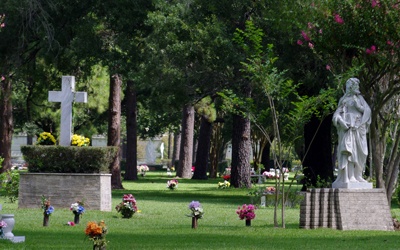
Traditional cemeteries allow upright monuments and markers that lie flush with the ground. The upright monuments are bold physical statements that enable passers-by to quickly recognize a cemetery.
Future Availability of Burial Space
Some properties have ample space to accommodate new interments for many years to come. These cemeteries can expect a steady revenue stream well into the future. Others are nearly full. Constructing new mausoleums and lawn crypts (see descriptions that follow) are ways to accommodate additional interments. However, these are expensive to build and may not be viable options.
Therefore, if you are looking for multiple sites for family members, ask about availability of space in the future or pre-purchase your cemetery property.
Perpetual Care Funds
Unlike other funeral service providers whose work is finished at the end of the funeral, burial parks must provide perpetual care for the grave site and the grounds. Cemeteries establish “perpetual (or endowment) care funds” to cover this cost to generate ongoing income. Calculating how much money must be set aside, or endowed, for a cemetery’s long-term care is not an exact science. Therefore, most States have laws requiring a minimum portion of each sale to be deposited to a care fund. Some cemeteries may be underfunded despite these State laws. This poses an unanswered question for our society, “what will happen if someday the money runs out to maintain a cemetery?”
Combined Operations
When a property owner constructs a funeral home in a cemetery, it is called a “combination operation.” These “combos” may provide certain efficiencies due to the common ownership and are a “one-stop” source for funeral services.
Whether or not combo operations should be allowed is a controversial industry issue. Some argue that combos promote competition and are good for consumers. Others believe that combos put the independent funeral home at an unfair disadvantage. With this in mind, some States have prohibited common ownership of funeral homes and cemeteries.
Cemetery Property
Following are the different types of cemetery property and a description of each:
Grave Space

A grave space, or burial plot, is a section of land in a burial park where the casket containing human remains and an outer container are buried. Some cemeteries allow two to be buried in one grave space. The size of grave spaces varies.
Crypts

Mausoleum crypts are placed inside a building known as a mausoleum, which is constructed for private families or entire communities. Mausoleums often have marble or granite facings and are sometimes decorated with sculpture and stained glass. Some have a chapel inside.

Garden Crypts are housed in an outdoor mausoleum. These are similar to indoor mausoleums, but the crypts are visited outside rather than inside.
Lawn Crypts are concrete enclosures that house caskets underground. They are similar to grave spaces. However, no outer burial container is used because the concrete enclosure serves the same purpose of supporting the earth.
Lawn crypts may be built for one or two persons and may be configured side-by-side and/or several levels deep.
Niches

A niche is a space for interment of cremated remains. Niches are constructed in a columbarium, a free-standing structure, or are housed in an area within a mausoleum.

Urns are often displayed in glass-enclosed niches inside a mausoleum.
Scattering Gardens

A scattering garden refers to a designated area in a cemetery where cremated remains can be scattered.



